| September 2010 Index | Home Page |
Editor’s Note: This paper examines the transformational role of technology in teaching and learning. Just as the printing press played a transformational role in the renaissance, do electronic technologies play a similar role in distance learning? The analysis presented here shows the importance of technology as a tool to support transformation.
Can Technology Transform Online Learners?
Victor C. X. Wang and Jim Berger
USA
Abstract
The most common misconception is that technology can transform online learners as the power of E-learning has been exaggerated in the 21st century. As an essential component of our social environment, technology can only help to transform online learners. In other words, it provides a powerful teaching/learning tool used to “enhance” learning, hence learners changed in the three most often talked about domains. This article argues that it is the learners themselves that seek perspective transformation via critical theory and epistemological positions in the virtual environment. Technology, together with online course instructors play a helping role in terms of helping learners attain changed behavior. Through the discussion of the above pertinent issues, an insightful model titled Learners’ Seeking Transformation via Web 2.0 Technologies, has emerged.
Keywords: instrumental, practical, communicative, emancipatory, epistemological, postpositivism, constructivism, advocacy/participatory, pragmatism, reflection, confucius, and transformation
Introduction
Researchers and educators have been grappling with the issue: can technology transform online learners? It is true that learners engage in online learning in order to seek change in Bloom’s (1956) three domains: 1, cognitive domain; 2, psychomotor domain; and 3, affective domain. In other words, for educators and researchers to find out whether online learners have learned anything from their online courses, they can ask the following questions:
Do the learners think differently after completing this online class?
Do the learners act differently after completing this online class?
Do the learners feel differently after completing this online class?
Evidently, the three questions revolve around the three domains of educational objectives. Once these objectives are achieved on the part of learners, we say that the learners are transformed. However, the question remains unanswered: who has transformed these online learners? Course instructors, Web 2.0 technologies or the learners themselves?
First of all, course instructors have been trained in a specific discipline. Then, given their knowledge base and instructional experience, they are hired by universities or colleges to “teach” online courses. To be successful in the online learning environment, they must possess a certain body of knowledge that they can impart to their learners one way or the other. In Western cultures, an instructor’s teaching is constantly evaluated by students. If instructors keep receiving low ratings from students, they may be subject to further training in the field. In rare cases, some unqualified instructors’ employment as professional teachers may be terminated. Those who remain in the academy based on consistently good teaching evaluations are considered knowledgeable in the field or have the ability to impress their students enough to warrant a good review of their teaching abilities. Above all, as teachers, they inspire learners to transform themselves via their teachings or serving as role models even in the virtual learning environment. There has been more than enough literature on how course instructors transform online learners.
What about technology? Can technology transform online learners? Since education was delivered in the early 21st century, scholars have been asking this question. Some say, “yes, technology transforms online learners in a big way.” Others say, “technology provides only teaching and learning tools; it is the learners that can seek transformation themselves.” Two lines of thought have been presented, but are subject to deeper exploration. It is true that too many exaggerations regarding the power of technology have been heard of in online teaching and learning environments. Some have become rather cliché. For example, people have been known to say, “technology will replace human beings.” “Technology will lead to the demise of the face to face classroom teacher.” “Intelligent computers will replace classroom teachers.” While some educators feel threatened by these exaggerations, others choose to explore the power of technology. In fact, programmed instruction started in the early 1960s with the advent of computers and behaviorist theory advanced by Watson and Skinner (1967; 1968). The literature regarding the power of technology in the past has revealed some central themes:
Learners study technology as technology represents a core body of knowledge.
Learners learn from technology as technology complements and supplements learners’ existing knowledge base.
Learners learn with technology as technology represents one access point to knowledge.
However, little has been written regarding whether technology can transform online learners. Since Marx advanced critical theory and Habermas advanced the three kinds of knowledge, Mezirow advanced the theory of transformative learning. The theory of transformative learning helps interpret how learners seek change in the three domains of educational objectives. Mezirow emphasizes perspective transformation, that is, the cognitive and affective domains. A brief summary of perspective transformation follows.
Transformative learning is a process (Mezirow, 2000) that describes how learners transform a habit of thought by redefining a problem and examining her/his own assumptions, content, or process for problem solving. Learners who progress through a transforming event critically reflect on their assumptions and examine their points of view to determine how they approached solving problems presented by that event. Those transformations may be all of a sudden or epochal or take place over time with small or incremental changes and shifts in one’s thought process. Steps that lead to a transformation typically begin with what Mezirow calls a “disorienting dilemma” (p. 22). From that dilemma, the learner examines his or her feelings and evaluates the assumptions that lead up to the disorienting dilemma. At this point, the person can ignore the event and its effects or recognize that they are not the only ones going through such an event and explore ways to prevent the disorienting dilemma from occurring again. If transformation is to take place, the person becomes a learner and sets out on a process of exploring new ways to approach the dilemma. Once new approaches are discovered, the learner can develop a plan, tries different approaches, learns from the experiences of the new approaches, and the learner becomes more skilled and competent in their newfound knowledge. As they work towards avoiding the disorienting dilemma, their new perspective and understanding is integrated back into one’s life. The core of the process of transformative learning is the use of critical reflection.
Perspectives are made up of frames of references or, “the structure of assumptions and expectations through which we filter sense impressions” (p. 16). Our frames of references are shaped by our experiences and how we interpret them and can represent cultural values or personal beliefs. Ones frame of reference is made up of two parts: habit of mind and points of view. Our habit of mind is based on the assumptions we hold regarding social, ethical, philosophical, psychological, and aesthetic values (Mezirow, 2000). Our point of view is how we express those assumptions. In other words, how we act upon those habits of mind becomes our point of view. Points of view are made up of a group of meaning schemes, or how we feel, believe, judge, or react to events or objects in the real world. As we are often times unaware of the meaning schemes we hold, they have the ability to impact how we interpret the world around us. Our meaning schemes inform our frame of reference and impact how we express those frames of references to the rest of the world. People rely on those frames of reference as a touchstone for their existence and sense of identity. When alternative points of view are expressed that challenge existing frames of reference, it is more likely that the person will disregard them. However, if a disorienting dilemma challenges those frames of reference to the point that they cannot be dismissed, it is likely the person will experience transformative learning.
Critics of the theory cite lack of consideration of social context. If technology is considered part of the social context, it comes back to the same question: Can technology transform online learners in relation to the theory of transformative learning?
In the field of adult education, what plays a major role in terms of learners’ transformation, technology or the learners themselves via epistemological positions? This article seeks to shed some light on how online learners seek to transform themselves through different epistemological positions in relation to the theory of transformative learning and even the much debated theory of andragogy advanced by Knowles (1970, 1975). It does not seek to underestimate the power of technology. Rather, technology provides excellent teaching and learning tools in the online environment. As Olgren (2000) indicates, “technology invites a tools-first emphasis, but technology is only as good as our knowledge of how to use it to enhance learning” (p. 7).
Theoretical Framework
For years, scholars and educators have been relying on the theory of andragogy (Knowles, 1984), or principles of adult learning, to help understand how learners seek change in the field. In the early 1990s, scholars such as Mezirow and Cranton began to advance a new theory, the theory of transformative learning to help interpret how learners seek transformation, especially a deep shift in perspective. According to Mezirow and Cranton (1991, 2000; 2010) the process of transformative learning focuses on critical reflection and critical self-reflection whereas other scholars may place imagination, intuition, and emotion at the heart of transformation (Dirkx, 2001). Although Mezirow’s theory was based on a study of women who found that their experience of returning to college led them to question and revise their personal beliefs and values in a fairly linear ten-step process, theoretically, he drew on Habermas’s (1971) three kinds of human interest and the resulting three kinds of knowledge—Instrument, practical, and emancipatory. The goal in using transformative learning theory is for learners to attain emancipatory knowledge by critically reflecting upon the first two kinds of knowledge—Instrumental and Practical (Communicative in Mezirow’s terms). Further, Mezirow addressed three types of meaning perspectives—epistemic (about knowledge and how we acquire knowledge), sociolinguistic (understanding ourselves and social world through language), and psychological (concerned with our perception of ourselves largely based on childhood experiences). Mezirow appears to focus more on the cognitive domain of educational objectives.
However, critics of Mezirow’s theory fail to understand that in order for learners to become meaningful doers, perspectives must be changed first. Consider Kacirek, Beck, and Grover’s quote, “even the early Greeks believed that working people didn’t think and thinking people didn’t work” (as cited in Kacirek, Beck, & Grover, 2010, p. 32). Although Mezirow was modest and humble by saying that his theory is a theory in progress, his emphasis on cognitive and affective domains was well justified by even early Greeks.
The next question to ask is how helpful is the theory of transformative learning when interpreting whether technology, as part of the social context, can transform learners. Or is it as powerful as the traditional theory of andragogy in terms of interpreting the relationship between technology and online learners? In the next section, we address how learners acquire knowledge in the virtual learning environment by reflecting on the theoretical framework.
Epistemological Positions and Online Learning
Learners engage in online learning for a variety of reasons. The asynchronous nature of online learning is so conspicuous and returning students especially enjoy this feature of online learning because of their multiple work/family responsibilities (Wang, 2006, 2008). Some employees take online courses because learners are limited to those courses provided via Blackboard or WebCT programs. Learners, as a result, can save money on gas and have the flexibility of taking asynchronous courses anytime throughout the day rather than adhering to a set schedule. Other learners take online courses because it is mandated by their employers. Those organizations that wish to remain competitive in this global economy must seek to train and retrain their employees in the new century. Having employees take university courses is a primary method of training employees. Needless to say that traditional age students can take online courses to attain career and life goals. Given the downturn of the economy, universities wishing to save money offer online courses and, thus, do not have to pay for brick and mortar buildings, construction of parking lots, nor their upkeep. All these reasons may point to one direction, that is, online learning as predicted by Knowles (1975) has become popular in the new century. And the popularity of online learning is driven by four epistemological positions: postpositivism, constructivism, advocacy/participatory, and pragmatism. These four positions are closely related to Mezirow’s theory of transformative learning. The heart of his theory is for learners to experience perspective change via critical reflection and critical reflection must be based on Habermas’s three kinds of knowledge and the four espitemological positions. Without interpreting the four positions, readers may wonder how learners engage in learning online via technology. It comes back to the central question: can technology transform online learners? By expanding the four positions in the following section, readers will see clearly that it is the learners who seek to transform themselves while technology is meant only to be used to enhance learning.
Postpositivists believe that knowledge is created by humans conjecturing and that, for learners to create an understanding, it is important that they work with and challenge the conjectures (Bettis & Gregson, 2001). In the virtual environment, course instructors can arrange knowledge by specifying course syllabus, course assignments, discussion topics, course evaluation methods and learning resources. Then online learners come to the virtual environment to study, observe and even challenge these conjectures in order to determine effects or outcomes. Course instructors justify the course’s existence by saying, “there are laws or theories that govern the world, and these need to be tested or verified and refined so that you, as learners, can understand the world.” If we try to connect this position with instructional methods, we can likely say that this position is in agreement with andragogy instead of pedagogy simply because instructors link learners to learning resources. Learners do the “legwork” by embarking on Habermas’s instrumental knowledge and practical knowledge in order to attain emancipatory knowledge—perspective transformation in Mezirow’s terms.
Constructivists assume that individuals seek an understanding of the world in which they live and work. Individuals develop subjective meanings of their experiences—meanings directed toward certain objects or things (Creswell, 2009, p. 8). Creswell further indicates that these meanings are varied and multiple, leading the learner to look for the complexity of views rather than narrowing meanings into a few categories or ideas. Based on this position, online learners’ tasks are clear: learners construct the meaning of a situation, typically forged in discussions or interactions with other persons. Then course instructors may arrange more open-ended questioning, case studies, analyzing personal experiences. These instructional methods all fit well with this position. In adult education, this epistemological position penetrated into the field a long time ago. When scholars address “experiential learning”, they want learners to make meaning out of their experience. Some universities in the United States grant college credits to adult learners based on experiential learning. If learners can turn their prior experience into knowledge, skills or attitudes, why require them to take redundant courses to waste their time or money? In the virtual learning environment, instructors may arrange learning activities around learners’ prior experience. Again, we can tell that learners seek change in the cognitive domain or affective domain based on the reflection of their experiential learning or prior learning. Technology is used as an external environment. To further elaborate on the constructivist position, we will focus on the following central themes:
Meanings are constructed by learners themselves as they engage with the virtual learning environment. Course instructors tend to use open-ended questions so that the learners can share their views and generate knowledge through their sharing.
Learners engage with the virtual learning environment and make sense of it based on their historical and social perspectives. Course instructors may remind learners to seek to understand the context or setting by visiting this context and gathering information personally via the use of technology.
The basic generation of meaning is always social, arising in and out of interaction with an online learning community. The goal of course instructors is to foster an online learning community.
Scholars and educators feel that postpositivist and constructivists do not go far enough in advocating for an action agenda to help marginalized peoples in society. Therefore, they developed advocacy/participatory worldview by drawing on the writings of Marx and Freire (Neuman, 2000). According to Creswell (2009), an advocacy/participatory worldview holds that learners need to become radical philosophers, that is, they need to have an action agenda for reform that may change the lives of themselves, the institutions in which they work or live, and perhaps the larger society. The course instructor’s role is to have learners speak to important social issues of the day, issues such as empowerment, inequality, oppression, domination, suppression, and alienation. Learners should be considered equals of their course instructors. Therefore, learners may help design online learning questions, collect data, and analyze information together with their course instructors in the online learning environment. Since this epistemological position focuses on the needs of the learners and learners in society that may be marginalized or disenfranchised, we can tell the ultimate goal of this position is for learners to develop emancipatory knowledge. Specifically, learners can seek to do the following in order to develop a perspective change:
Learners advance an action agenda for change based on this worldview.
Learners seek to free themselves from constraints found in the media, in language, in work procedures, and in the relationships of power in educational settings.
Learners began with an important issue or stance about the problems in society.
Learners seek to create a political debate so that real change will occur.
Course instructors consider their learners as active collaborators in the learning process in the virtual environment.
The fourth epistemological position is pragmatism that maintains that a worldview arises out of actions, situations, and consequences rather than antecedent conditions as in postpositivism (Creswell, 2009). Learners are required to use all approaches available to understand problems. To understand problems, learners are free to choose the methods, techniques, and procedures that best meet their needs or purposes. Learners may use multiple methods to understand a particular problem. The emphasis in pragmatism is on hands-on application and practical solutions to problems rather than esoteric or theoretical approaches.
In summary, the four epistemological positions together with the theory of transformative learning and principles of andragogy all translate into instructional methods either in the traditional classroom setting or virtual learning environment. These positions view knowledge acquisition differently, yet they share some commonality. It seems that no single position seeks to specify pedagogical instructional methods. Rather, they all prompt course instructors to provide “andragogical” instructional methods, which were vividly described by Knowles, Holton and Swanson (1998) as follows:
Finally, I found myself performing a different set of functions that required a different set of skills. Instead of performing the function of content planner and transmitter, which required primarily presentation skills, I was performing the function of process designer and manager, which required relationship building, needs assessment, involvement of students in planning, linking students to learning resources, and encouraging student initiative. (p. 201)
Indeed, both instructors and technology play a helping role rather than a directing role in the virtual learning environment (Wang, 2005). For any change in the three domains of educational objectives to occur, it is the learners that seek to transform themselves and their transformation can be clearly expounded by the prevalent theories or epistemological positions.
The following model has emerged from this article and several points are worth emphasizing:
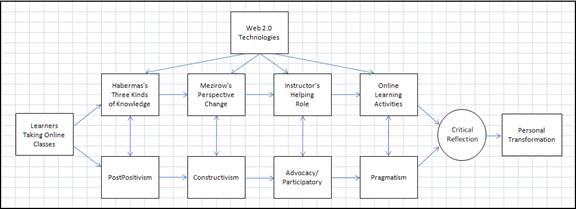
Model One: Learners’ Seeking Transformation via Web 2.0 Technologies
Technology as a teaching/learning took provides an interactive learning environment to enhancing learning.
Instructors play a secondary helping role by providing a conducive environment via putting their course syllabi, assignments and discussion forums online.
It is the learners that seek to transform themselves and their transformation is driven by learning theories and epistemological positions.
Change, whether more in cognitive or affective domains, is bound to occur because of the nature of epistemological positions and our worldviews.
Relying too much on technology without taking into consideration learning theories or epistemological positions will prevent instructors from prescribing the much needed andragogical instructional methods.
What really contributes to learners’ transformation is the learners themselves. Change must come from within the learners not from outside the learners.
Further Reflections
Technology was designed and built by intelligent humans and it is supposed to serve the learning needs of learners and instructional needs of instructors in this information age. We have advanced into this information age simply because education is being delivered electronically. And technology has permeated society in general, and major government and economic stakeholders have recognized the importance of incorporating technology throughout education in order to prepare a competitive workforce in a global economy (Farmer, 2010, p. 276). However interactive technology can be used in the teaching/learning arena, it is only one access point to knowledge, skills and attitudes. Learners have to do the learning in order to achieve perspective transformation in Mezirow’s terms. Learners learn in traditional classroom settings and learners learn in virtual environment. If learners are not motivated to learn, if learners are not self-directed to learn and if learners do not use the basic five senses to acquire knowledge, perspective transformation is not likely to occur. What really contributes to learners’ transformation are Habermas’s three kinds of knowledge, Mezirow’s interpretation of critical reflection, epistemological positions and even Knowles (1984) principles of andragogy. As a tool to enhance learning, technology does play a major role. However, technology itself can not enable transformation of online learners if learners are not engaged in actual learning themselves. As a tool, learners should take advantage of it. Some senior learners may get scared when thinking of learning via technology. Some younger learners may take technology for granted, believing they can be multi-tasked in terms of learning. Having the right attitude towards using technology as a tool to enhance learning is key to successful perspective transformation on the part of learners.
In addition to learning to be technology savvy, learners need to be internally motivated to learn. Confucius’s “silent reflection” is not outmoded in terms of promoting transformative learning. Schutz (1967) argues, “I live in my Acts and by reflecting upon them” (p. 51). Once we do this, we begin the process of critical reflection or meaning-making in our lives. The process of meaning making is a great way to transform oneself and it is such an essential part of the theory of transformative learning. Although technology serves as one access point to knowledge, it can also serve as a subject matter for learners. Do we not have universities where instructional technology is treated as an academic discipline? Learners can even obtain doctorate degrees in technology. Once learners obtain their degrees, they can practice in the field of technology. Professionals in the field teach “technology” as a subject. A subject of an academic discipline does not seek to transform online learners if learners decide to have nothing to do with it. It is when learners have made learning decisions to study such a subject or academic discipline that perspective transformation can begin to occur. To achieve three domains of educational objectives, learners need to be immersed in learning the subject matter. After this rigorous process of learning, learners can be totally transformed. Technology as an enhancing tool also provides a learning environment. As to whether learning will occur, Rogers’ 1969 hypotheses regarding learning should be taken into consideration on the part of online instructors:
Human beings have a natural potential for learning. They are curious about their world, until and unless their curiosity is blunted by their experience in our educational system. They are ambivalently eager to develop and learn. The reason for the ambivalence is that any significant learning involves a certain amount of pain, either pain connected with the learning itself or distress connected with giving up certain previous learnings.
Significant learning takes place when the subject matter is perceived by the student as relevant for his/her own purpose. A person learns significantly only those things which he perceives as being involved in the maintenance of, or the enhancement of, his own self.
Learning which involves change in self-organization—in the perception of oneself—is threatening and tends to be resisted.
Those learning experiences, which are threatening to the self, are more easily perceived and assimilated when external threats are at a minimum.
When threats to the self are low, experience can be perceived in a different fashion and learning can proceed.
Much significant learning is acquired through doing.
Learning is facilitated when the student participates responsibly in the learning process.
Self-initiated learning which involves the whole person of the learner—feelings as well as intellect—is the most lasting and pervasive.
Independence, creativity, and self-reliance are all facilitated when self-criticism and self-evaluation are basic and evaluation by others is of secondary importance.
The most socially useful learning in the modern world is the learning of the process of learning, a continuing openness to experience and incorporation into oneself of the process of change.
All these hypotheses are important, but involving the whole learner—feelings as well as intellect should be the most important in terms of helping learners achieve perspective transformation. Without going through this process, learners’ behavior can be changed to a certain extent. As Rogers put it, to achieve the most lasting and pervasive change, learners should involve the whole person in learning. To do so, learners also need to be engaged on multiple levels and with multiple experiences and technology can help provide those experiences.
Conclusion
This article has posited that technology cannot transform online learners. Rather, it is the learners themselves that can transform themselves by using technology as a tool to enhance learning. The theory of transformative learning has developed as a different branch of the theory of andragogy in adult education. It is based on Habermas’s three kinds of knowledge, Marx’s critical theory and Freire’s radical philosophy. Learners seek to transform themselves via four epistemological positions. No one single theory of learning is more important than another. As Knowles’s prediction about E-Learning came true in the new century, technology has provided an additional learning environment for learners to engage in transformative learning. In a sense, this additional access point to knowledge has accelerated learning, which means that learners do learn at a faster pace than in the past when technology was not available. Learning anywhere, anytime is needed in the information age when speed is used to measure learning or progress. It took Chinese engineers many years to develop faster trains and now their trains “fly” at the speed of 353 kilometers per hour. Suppose learners take these trains to go to schools to learn certain academic subjects. Well, learning can be accelerated because of these faster trains—new technology. More time gained by taking faster trains means learners can spend more time on critical reflection. Does more time on critical reflection mean more learning? Supposedly so. According to
References
Bettis, P. J., & Gregson, J. A. (2001). The why of research: Paradigmatic and pragmatic considerations. In E.
Bloom, B. S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals – Handbook one: Cognitive domain. New York: Longman.
Cranton, P. (2010). Working towards self-evaluation. In V. C. X. Wang (Ed.), Assessing and evaluating adult learning in career and technical education (pp. 2-11). Hangzhou, China; Hershey, USA: ZUP and Information Science Reference.
Creswell, J. W. (2009). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research (3rd ed.). Los Angeles: SAGE.
Dirkx, J. (2001). Images, transformative learning and the work of soul. Adult Learning, 12(3),
15-16.
Farmer, L. (2010). Career and technical education technology: Three decades in review and technological trends in the future. In V. C. X. Wang (Ed.), Definitive readings in the history, philosophy, practice and theories of career and technical education (pp. 259-277). Hangzhou, China; Hershey, USA: ZUP and Information Science Reference.
Habermas, J. (1971). Knowledge and human interests. Boston: Beacon Press.
Kacirek, K., Beck, J. K., & Grover, K. S. (2010). Career and technical education: Myths, metrics, and metamorphosis. In V. C. X. Wang (Ed.), Definitive readings in the history, philosophy, practice and theories of career and technical education (pp. 31-49). Hangzhou, China; Hershey, PA: ZUP and Information Science Reference.
Knowles, M. S. (1970). The modern practice of adult education: Andragogy versus pedagogy. New York, NY: Association Press.
Knowles, M. S. (1975). Self-directed learning: A guide for learners and teachers. New York, NY: Association Press.
Knowles, M. S. (1984). Introduction: The art and science of helping adults learn. In M. S. Knowles & Associates (Eds.), Andragogy in action (pp. 1-21). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Knowles, M. S., Holton, E., & Swanson, A. (1998). The adult learner. Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing Company.
Mezirow, J. (1991). Tranformative dimensions of adult learning. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Mezirow, J. (2000). Learning to think like an adult. In J. Mezirow & Associates (Eds.), Learning as transformation: Critical perspectives on a theory in progress (pp. 3-34). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Neuman, W. L. (2000). Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches
(4th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Olgren, C. H. (2000). Learning strategies for learning technologies. In E. J. Burge (Ed.), The strategic use of learning technologies (pp. 7-16). New Directions for Adult Continuing Education, No. 88. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Rogers, C. R. (1969). Freedom to learn. Columbus, OH: Merrill.
Schutz, A. (1967). The phenomenology of the social world. London: Heinemann.
Skinner, B. F. (1968). The technology of teaching. New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Tu, W. M. (1979). Humanity and self-cultivation: Essays in Confucian thought. Berkeley: Asian Humanities Press.
Wang, V. C. X. (2006). Essential elements for andragogical styles and methods: How to create andragogical modes in adult education. Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Wang, V. C. X. (2008). Facilitating adult learning: A comprehensive guide for successful instruction (Rev. ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Watson, G. (Ed.). (1967). Concepts for social change. Washington, D.C.: National Training Laboratories Institute for Applied Behavioral Science.
About the Authors
| Dr. Victor Wang is Associate Professor, Department of Teacher Education,t California State University, Long Beach, CA. His research and writing have focused on workforce education, foundations of adult education, adult teaching and learning, training, transformative learning, cultural issues in vocational and adult education, distance education, human performance technology and curriculum development. He has published over 100 journal articles, book chapters and books during his eight years at CSULB and is reviewer for five national and international journals. Currently he serves as the editor in chief of the International Journal of Adult Vocational Education and Technology. He has won academic achievement awards from universities in China and in the United States. E-mail: cwang@csulb.edu |
| Jim Burger, Ph.D. is Associate Professor at Western Kentucky University. He developed and now manages an online Master of Arts program in Adult Education. E-mail: jim.berger@wku.edu |

